Antarctica is often seen as a barren, frozen expanse — but there’s more to this icy continent than meets the eye. This article unravels 19 surprising truths about Antarctica that challenge conventional perceptions. From its unique wildlife to unexpected phenomena, each revelation paints a richer picture of a land shrouded in mystery and wonder. Prepare to be amazed by the secrets lurking beneath the ice and the stories waiting to be told.
1. The Warmth Beneath
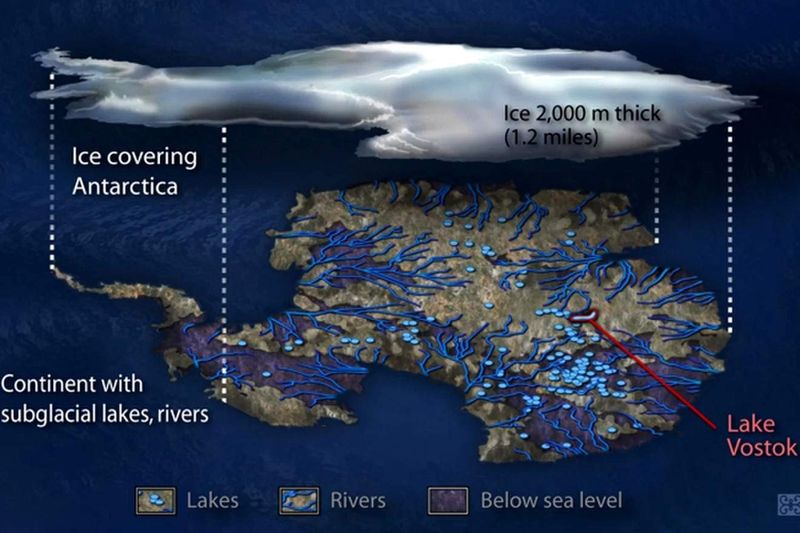
Beneath Antarctica’s icy facade lies a secret warmth. Geothermal heat seeps from the Earth’s crust, creating unique subglacial lakes. These lakes are teeming with microbial life, thriving in isolation. This hidden warmth challenges our understanding of life in extreme conditions.
Scientists have discovered over 400 such lakes, each a biological treasure trove. The largest, Lake Vostok, remains a focus of fascination. Its isolated ecosystem hints at possibilities for extraterrestrial life on icy moons.
This geothermal activity also affects ice flow, influencing global sea levels. It’s a reminder of the dynamic interactions shaping our planet.
2. The Dry Valleys
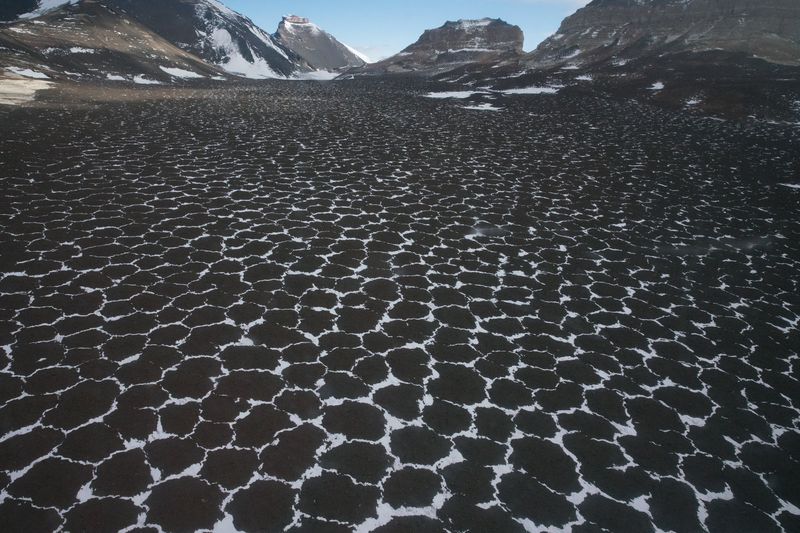

Amidst Antarctica’s icy expanse lie the McMurdo Dry Valleys, one of the continent’s most extreme environments. Surprisingly, these valleys receive almost no precipitation, making them hyper-arid. Winds gust at speeds over 200 mph, stripping moisture from the land.
This region closely resembles the surface of Mars, attracting scientists eager to study its unique geology. Life here is sparse but resilient, with specially adapted microbes surviving in salt-laden waters.
The McMurdo Dry Valleys offer a glimpse into Earth’s past climate and potential future changes, serving as a natural laboratory for climate research.
3. Blood Falls
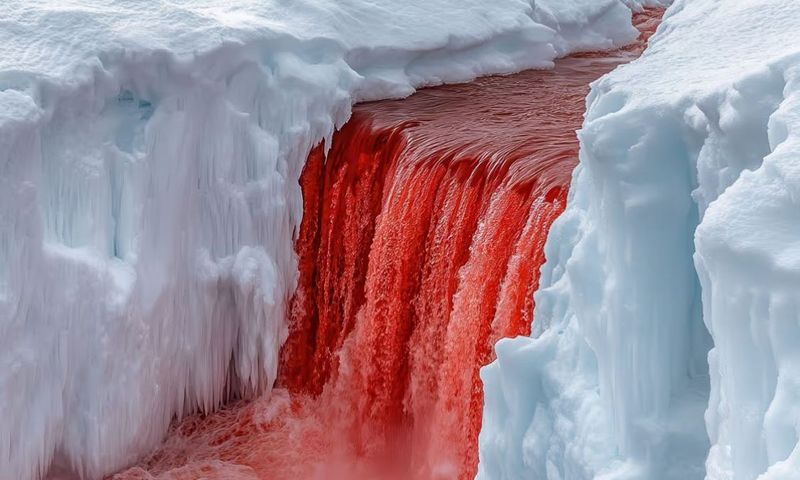

Blood Falls, a hauntingly beautiful phenomenon, stains the white Taylor Glacier with its crimson hue. This striking waterfall owes its color to iron-rich saltwater, oxidizing upon contact with air.
Originating from a subglacial lake trapped for millennia, Blood Falls offers a rare glimpse into ancient microbial ecosystems. These microorganisms thrive without sunlight or oxygen, metabolizing sulfur and iron.
This discovery fuels curiosity about life’s adaptability, providing clues for astrobiology. Blood Falls is a vivid testament to the hidden wonders beneath Antarctica’s icy surface, challenging assumptions about life in extreme environments.
4. Antarctic Oases
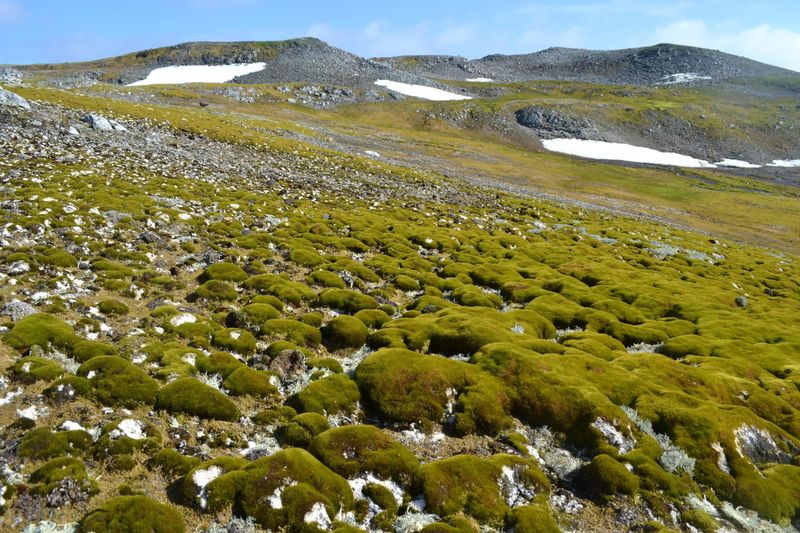

In stark contrast to its icy surroundings, Antarctica hosts verdant oases. Along the coast and on exposed mountain ridges, patches of green flourish. Mosses and lichens dominate these areas, showcasing life’s tenacity.
These biological hotspots contribute significantly to the continent’s biodiversity. They offer insights into primitive plant resilience and the evolution of photosynthesis.
Antarctic oases are crucial for understanding plant survival strategies in harsh climates. They remind us that life can persist in unexpected places, defying the harshest conditions. These pockets of life are crucial to ecological research and conservation efforts.
5. The Singing Ice

Antarctica’s ice sheets are alive with sound. Known as the “singing ice,” vibrations within the ice produce eerie, haunting melodies. These sounds result from wind and temperature shifts causing the ice to crack and creak.
Researchers monitor these acoustic emissions to study ice dynamics and stability. Understanding these sounds helps scientists predict ice flow patterns and potential iceberg calving events.
The singing ice also captivates artists and musicians, inspiring compositions that blend nature’s music with human creativity. This phenomenon highlights the intersection of science and art, where nature’s voice becomes a muse.
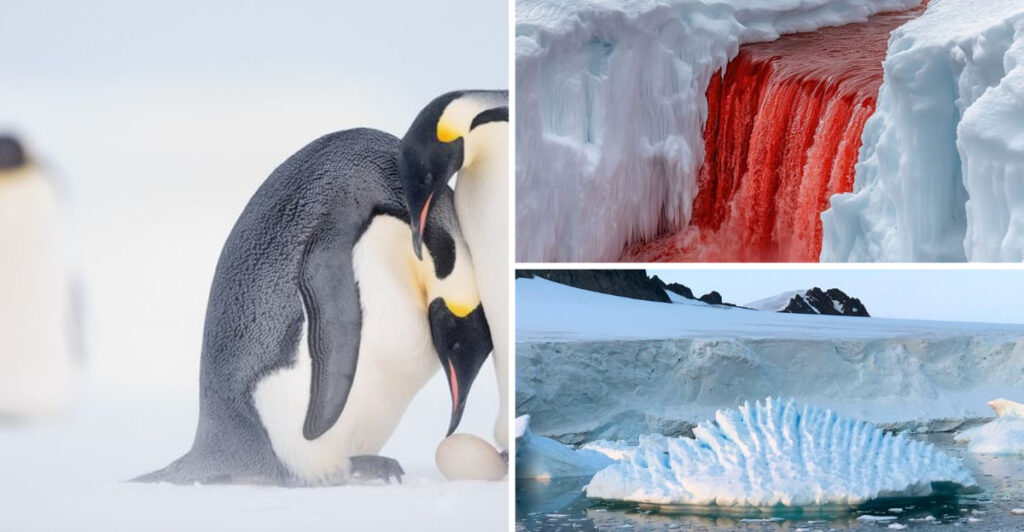
6. The Emperor’s March
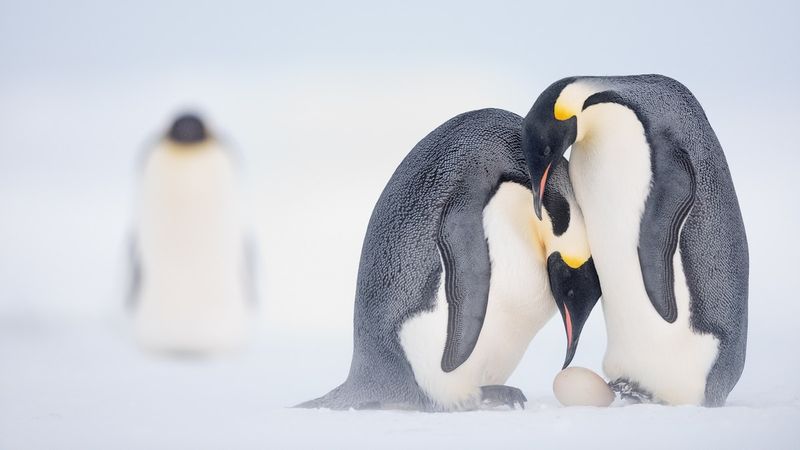

Antarctica is home to the iconic Emperor penguins, known for their remarkable endurance. Each year, these birds undertake a treacherous journey to breed, marching over 50 miles across the ice.
Their survival story is one of cooperation and resilience. During the harsh winter, males incubate eggs on their feet, huddling together for warmth while females hunt at sea.
This cycle of life is a testament to nature’s adaptability and the strength of communal bonds. Emperor penguins embody the spirit of Antarctica, thriving in one of Earth’s most unforgiving climates.
7. A Frozen Time Capsule
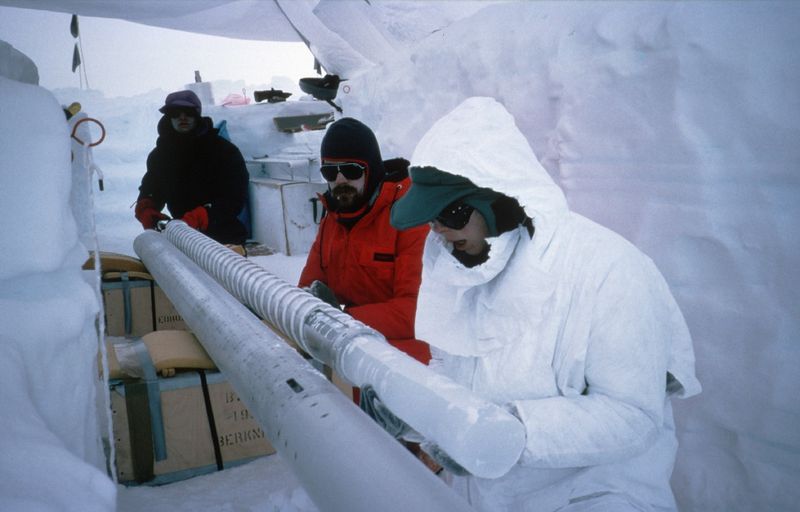

Antarctica’s ice sheets serve as frozen time capsules, preserving Earth’s climatic history. Scientists drill into the ice to extract cores, revealing atmospheric conditions from hundreds of thousands of years ago.
These ice cores contain trapped air bubbles, offering insights into past greenhouse gas levels and temperature fluctuations. This data is critical for understanding climate change and predicting future trends.
The study of ice cores transforms our knowledge of Earth’s past, providing context for our current environmental challenges. Antarctica’s ice holds the keys to unlocking secrets of ancient climates and guiding future actions.
8. Life in the Dark
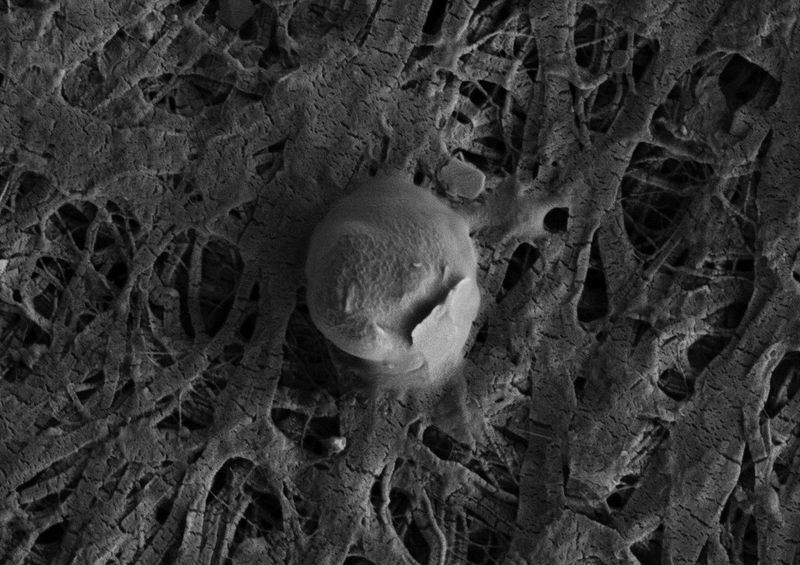
Hidden beneath Antarctica’s ice are subglacial lakes, harboring life in perpetual darkness. These ecosystems, isolated for millions of years, house unique microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions.
Scientists study these lakes to understand life’s potential on other planets and moons. The discovery of metabolizing microbes without sunlight challenges our definitions of habitable environments.
These subglacial worlds are natural laboratories for astrobiology, offering clues about life’s resilience and adaptability. They remind us of the diversity and tenacity of life, even in the most inhospitable places.
9. The Wandering Pole
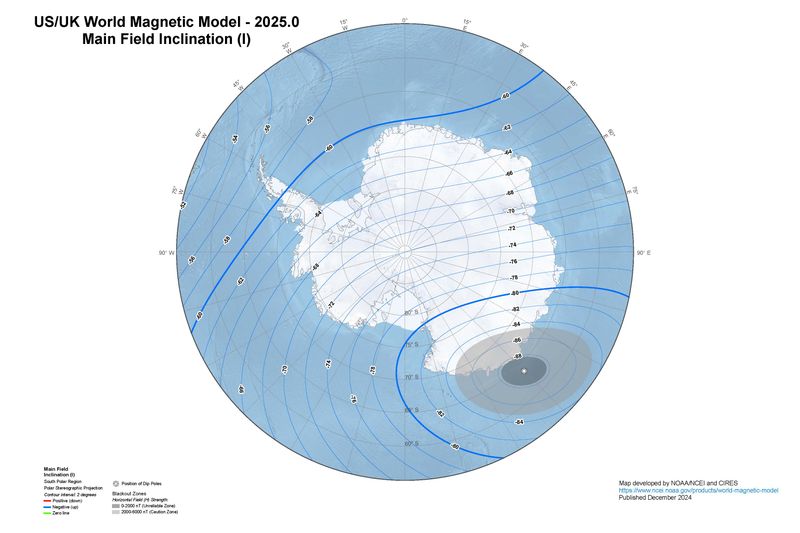
The magnetic South Pole is not fixed; it wanders unpredictably across Antarctica. This movement is due to fluctuations in Earth’s molten core, which generates the magnetic field.
Tracking the pole’s journey helps scientists understand geomagnetic phenomena and its impacts on navigation systems and animal migrations.
The wandering pole challenges traditional notions of stability, reminding us of the dynamic forces shaping our planet. It underscores the importance of ongoing research to anticipate changes affecting technology and ecosystems worldwide.
10. The Antarctic Desert
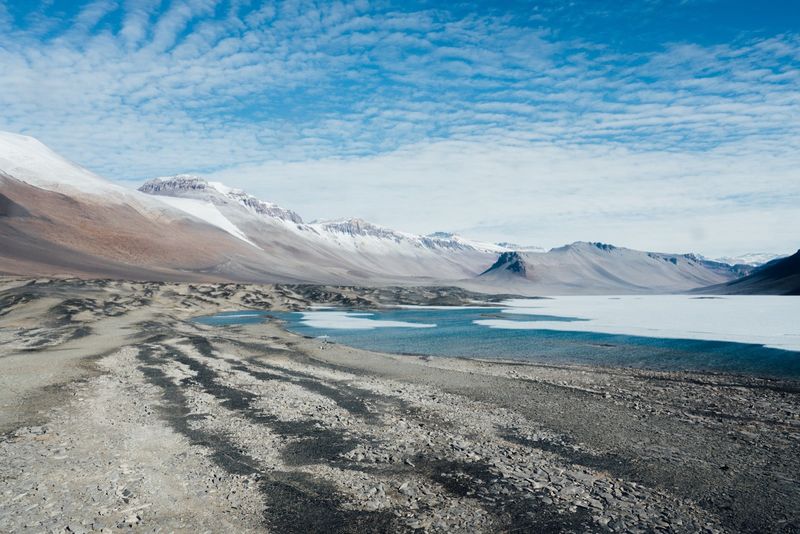

Despite being covered in ice, Antarctica is the driest continent on Earth. It qualifies as a desert, receiving less than 2 inches of precipitation annually.
This paradoxical reality creates unique challenges for life, making Antarctica an extreme desert environment. Its stark landscapes offer insights into desertification processes and climate adaptation.
Understanding Antarctica’s dry conditions helps scientists study water cycles and their impacts on global ecosystems. This knowledge is vital for predicting how climate change might alter precipitation patterns worldwide.
11. Antarctic Fossils

Antarctica was not always frozen. Fossils reveal that it once hosted lush forests and diverse wildlife. These remnants offer a window into Earth’s prehistoric past, showcasing a time when Antarctica was warm and green.
Paleontologists uncover plant and animal fossils that rewrite our understanding of continental drift and climate evolution. This evidence supports theories of past global warming events.
The study of Antarctic fossils provides context for current climate changes, highlighting the planet’s dynamic history. It reminds us of nature’s resilience and the potential for recovery in changing environments.
12. The Antarctic Treaty

In 1959, the Antarctic Treaty established Antarctica as a zone of peace and scientific collaboration. Signed by 12 nations, the treaty prohibits military activity and promotes research.
This unprecedented agreement fosters international cooperation and a shared commitment to preserving Antarctica’s pristine environment. It serves as a model for future global agreements on environmental protection.
The Antarctic Treaty underscores the importance of diplomacy and shared goals in tackling global challenges. It inspires a vision of unity and stewardship for our planet’s most fragile ecosystems.
13. The Icy Labyrinth

Antarctica’s ice formations create a mesmerizing labyrinth of crevasses and ridges. These features result from constant movement and pressure, sculpting the ice into complex patterns.
Navigating this icy maze poses challenges for explorers and researchers, requiring specialized skills and equipment. The formations also offer insights into ice dynamics and the forces shaping polar landscapes.
The icy labyrinth is a symbol of nature’s artistry, where science meets aesthetics. It captivates adventurers and scientists alike, revealing the intricate beauty hidden within Antarctica’s frozen expanse.
14. The Southern Aurora

Antarctica offers a front-row seat to the stunning Southern Lights, or Aurora Australis. These vibrant displays of color result from solar particles colliding with Earth’s atmosphere.
The auroras captivate those lucky enough to witness them, painting the sky with greens, reds, and purples. They provide valuable data for studying solar activity and its effects on Earth.
The Southern Aurora is a reminder of the beauty and interconnectedness of our solar system. It underscores the importance of scientific exploration in understanding cosmic phenomena and their impacts on our planet.
15. The Lost Meteorites
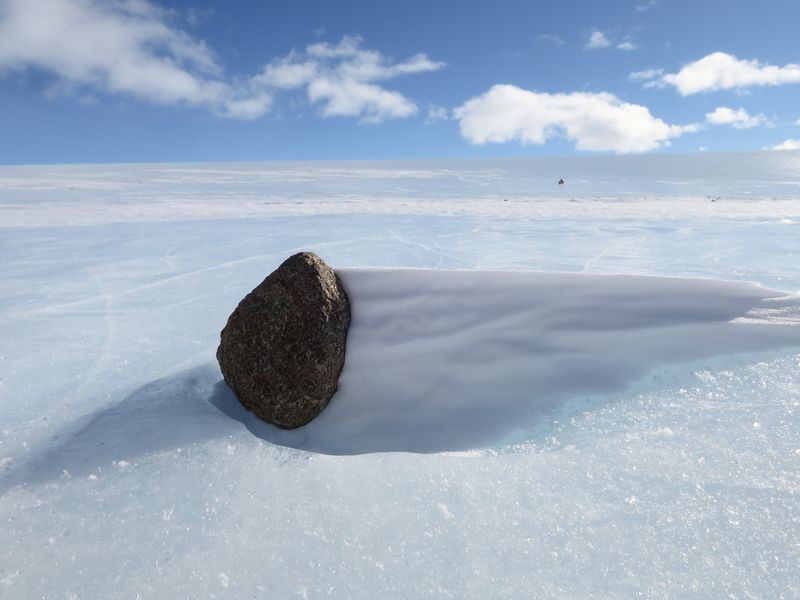

Antarctica is a treasure trove for meteorite hunters. The pristine ice contrasts with dark meteorites, making them easier to spot.
These space rocks offer insights into the origins of our solar system and the building blocks of planets. Scientists analyze meteorites to unlock secrets about cosmic history and planetary formation.
The search for meteorites in Antarctica highlights the continent’s role in advancing space science. It connects Earth’s most remote places with the mysteries of the universe, reminding us of our shared cosmic heritage.
16. The Antarctic Icefish
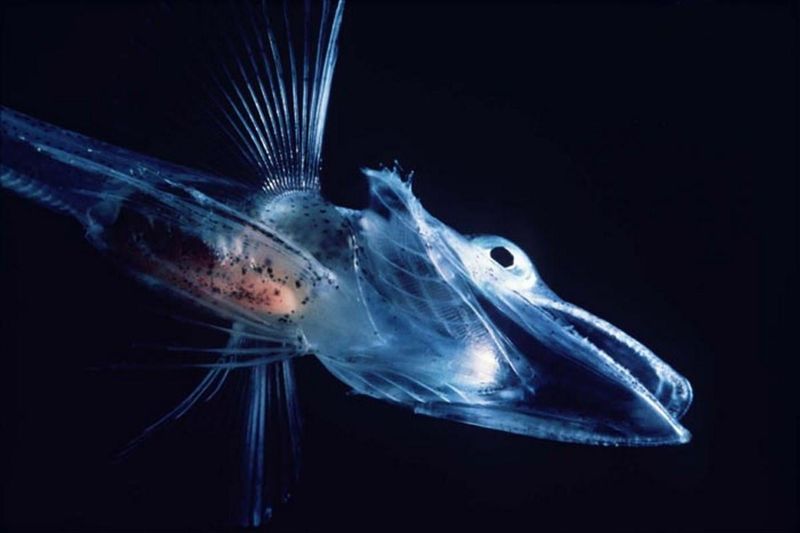

The Antarctic icefish is a marvel of evolutionary adaptation. Unlike most fish, it lacks red blood cells, relying on dissolved oxygen in the cold water.
This adaptation gives the icefish its transparent appearance, allowing it to thrive in frigid waters. Its unique physiology fascinates biologists studying life in extreme conditions.
The icefish exemplifies nature’s ingenuity, where survival hinges on inventive solutions to environmental challenges. It highlights the diverse strategies life employs to conquer the harshest habitats.
17. The Iceberg Graveyard

Antarctica is home to the “iceberg graveyard,” where colossal icebergs become stranded in shallow waters. These floating giants slowly melt, shaping the seascape with their towering presence.
The graveyard serves as a natural laboratory for studying iceberg dynamics and their impacts on marine ecosystems. Ocean currents and wind influence the journey of these icy behemoths.
The iceberg graveyard reminds us of the transient nature of ice, constantly changing and reshaping our planet’s oceans. It underscores the importance of understanding ice behavior in the context of global climate change.
18. The Polar Plateau
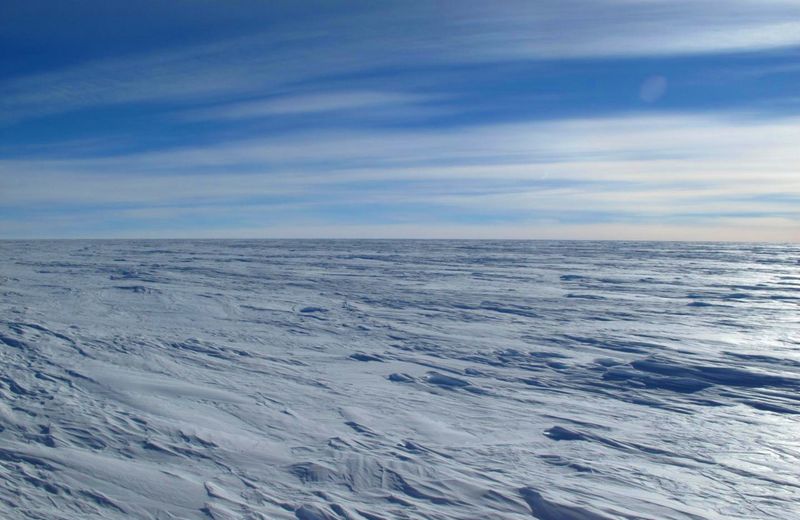

Antarctica’s Polar Plateau stretches across the continent’s heart, a vast expanse of flat ice. Temperatures plummet here, reaching some of the coldest recorded on Earth.
This plateau is a focal point for climate research, offering insights into atmospheric processes and temperature extremes. Its isolation provides a pristine environment for scientific studies.
The Polar Plateau symbolizes the stark beauty and isolation of Antarctica, challenging our perceptions of accessibility and survival. It represents the ultimate frontier for explorers and researchers seeking to unravel the continent’s mysteries.
19. The Ghost Mountains
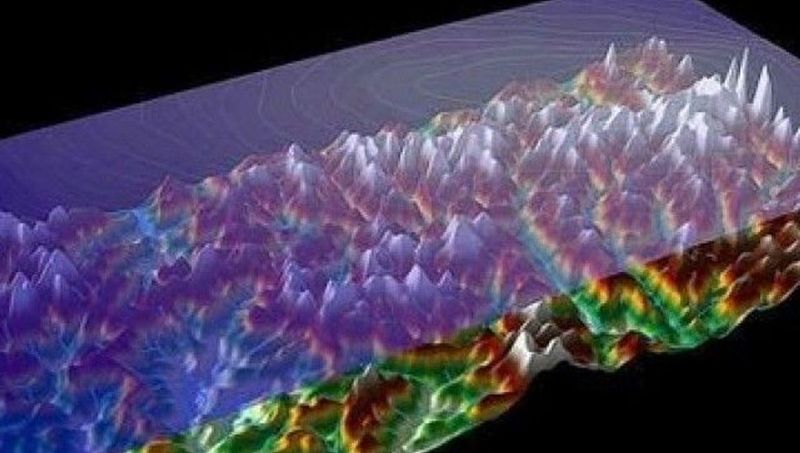

Beneath Antarctica’s icy veneer, the Gamburtsev Mountain Range remains a riddle wrapped in an enigma. Discovered in the mid-20th century, these ‘Ghost Mountains’ are hidden entirely under the ice sheet, unseen by human eyes.
Despite being buried under thousands of meters of ice, their peaks reach as high as the Alps. Scientists are baffled by their origin, considering Antarctica’s flat ice surface.
This submerged range challenges our understanding of geology and ice dynamics. Did you know? Their existence was first hinted by seismic surveys during the International Geophysical Year of 1957-58.



